





 Share
Share
2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium(IOS)











Highlights


Introduction
Location: The ADA Forsyth Institute, 245 First St, Cambridge (Boston), MA 02142.
Date: Saturday, October 5th and Sunday, October 6th, 2024.
The International Orthodontics Foundation (IOF) and the ADA Forsyth Institute are delighted to extend the official invitation to you for the upcoming 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium.
Organizers

International Orthodontics Foundation (IOF)
The International Orthodontics Foundation (IOF) is a not-for-profit organization devoted to improving orthodontic care around the world. The IOF enables, empowers and inspires clinicians by providing educational programs, promoting technology and innovation, and creating a global collaboration network.
With a rapidly growing global presence, IOF is inclusively open to all orthodontic clinicians. As of December 2023, we have over 13,000 members located in more than 110 countries and regions across all continents, with particular strength in North America, Europe and Asia.

The ADA Forsyth Institute
Mr. Donald Huang
Dr. Wenyuan Shi
Dr. Raymond Cohlmia
Prof. Michael Cima
Dr. Seung-Hak Baek
Dr. Daniela Garib
Dr. Peter Ngan
Dr. Ben Wu

ADA Forsyth Institute designates this activity for 10 continuing education Credit. Credit are awarded on actual attendance at individual sessions.
Concerns or complaints about a CE provider may be directed to the provider or to the Commission for Continuing Education Provider Recognition at ADA.org/CERP."

- This topic will explain the application of artificial intelligence technology in clinical orthodontics from the following four aspects:
- Customized Treatment Planning: Artificial intelligence can assist dentists in designing customized treatment plans by analyzing and learning from a large amount of clinical data. Based on information such as the patient's oral situation, medical history, and clinical symptoms, intelligent systems can predict the treatment outcomes for different cases and provide recommendations to dentists, thereby improving the precision and effectiveness of treatments.
- Assisted Diagnosis and Image Analysis: AI technology plays a crucial role in the field of oral imaging diagnosis. It can help clinicians analyze and diagnose X-rays, CT scans, and other imaging results. Intelligent systems can quickly and accurately detect issues such as malocclusions and skeletal discrepancies, providing clinicians with more accurate diagnostic results.
- Orthodontic Record Management and Treatment Progress Monitoring: Orthodontic treatment usually requires a prolonged period, and AI can monitor treatment progress in real-time by analyzing patients' oral imaging data. Intelligent systems can automatically recognize the movement of teeth and the fit of orthodontic appliances, etc. It can discover problems in the treatment process in time and provide clinicians with corresponding suggestions and corrections.
- Orthodontic Education and Training: AI can also be used in patient simulation through augmented reality devices, allowing dentists to practice in a virtual environment. The intelligent simulation of patients' skin, muscles, nerves, teeth, periodontal tissues, and joints can comprehensively display changes caused by orthodontic treatment. Enhanced reality mechanical sensors can make trainees feel the authenticity of the clinical environment, helping to improve the clinical skills of orthodontic students and dentists.
- Customized Treatment Planning: AI assists in designing personalized treatment plans by analyzing extensive clinical data, improving the precision and effectiveness of orthodontic treatments.
- Assisted Diagnosis and Image Analysis: AI enhances the accuracy and speed of diagnosing orthodontic issues through advanced image analysis of X-rays, CT scans, and other imaging results.
- Orthodontic Record Management and Progress Monitoring: AI monitors treatment progress in real-time, automatically recognizing changes in teeth movement and appliance fit, and providing timely suggestions for adjustments.
- Orthodontic Education and Training: AI, through augmented reality, offers realistic simulations for orthodontic training, enhancing the clinical skills of students and dentists by allowing practice in a virtual environment.

- Impact of Digital Technology: Over the past two decades, digital technology has greatly influenced orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Virtual to Physical: Virtual treatment plans are now commonly translated into digitally driven appliance manufacturing and placement through CAD/CAM techniques.
- Practical Applications: Dr. Ngan will demonstrate how clinicians can apply these technologies in everyday orthodontic practice using real case examples.

- Significant Impact of Technological Advances: Modern orthodontic practices have been greatly influenced by recent technological innovations.
- Major Innovations:
Digital Orthodontics: Incorporation of digital tools and techniques in orthodontic practice.
Artificial Intelligence: Utilization of AI to enhance diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care.
Direct-Printed Shape Memory Aligners: Advanced aligners created through direct printing technology.
Facial Scanners: Tools for capturing detailed 3D images of patients' faces.
Orthodontic Intraoral Devices: Innovative devices designed for improved treatment outcomes.
- Role of Evidence-Based Research: Contemporary orthodontic practices are shaped by research and prospective studies, ensuring treatments are backed by solid evidence.
- Focus of the Presentation: The presentation will specifically discuss the roles of digital orthodontics and direct-printed aligners in modern orthodontic practice.

Objective
To investigate the antibacterial and enamel remineralization performances as well as physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of a fluoride-coated clear aligner plastic (FCAP).
Materials and methods
FCAP and normal clear aligner plastic (CAP) were made by an aligner company. The FCAP was observed under SEM. Its element composition, resistance to separation, contact angle, and protein adhesion performance were characterized. CFU count and MTT assay were used to evaluate the antibacterial ability. Apatite formation was evaluated after immersing FCAP in artificial saliva. Enamel remineralization capability was evaluated in the demineralization model and pH cycling model. Cell CCK-8 and live/dead cell staining kits were used for cytotoxicity assay.
Results
The FCAP showed uniformly distributed fluoride and did not compromise protein adhesion performance. CFU and MTT assay indicated that the FCAP had stronger antibacterial activity. The FCAP could induce the formation of hydroxyapatite in artificial saliva and could reduce the microhardness decrease, color change, and mineral loss of enamels in both two models. CCK-8 and live/dead cell staining analyses showed that the coating did not compromise the biocompatibility of the clear aligner.
Conclusions
The FCAP had antibacterial, fluoride recharge, and enamel remineralization abilities while it did not compromise physicochemical properties and biocompatibility.
- Antibacterial Performance: The fluoride-coated clear aligner plastic (FCAP) demonstrated enhanced antibacterial activity compared to standard clear aligner plastic (CAP).
- Enamel Remineralization: FCAP effectively promoted the formation of hydroxyapatite in artificial saliva, leading to better protection against enamel demineralization, reducing microhardness loss, color change, and mineral loss.
- Physicochemical Properties: The fluoride coating on FCAP was uniformly distributed and did not negatively impact its protein adhesion or other key physical properties.
- Biocompatibility: The FCAP maintained good biocompatibility, with no harmful effects on cell viability as confirmed by cytotoxicity assays (CCK-8 and live/dead cell staining).
- Overall Conclusion: FCAP provides both antibacterial and enamel remineralization benefits while preserving the essential physicochemical properties and biocompatibility required for clear aligners.

- Material Properties and Biomechanics: The essential principles of aligner material properties and biomechanics will be revisited for the audience to ensure a solid foundational understanding.
- Current and Future Applications: Discussion on both present and future applications of 3D printed aligner technology, providing a comprehensive view of its potential in orthodontics.
- Independent and Reliable Data: The goal is to share independently tested and reliable data with AAO members, offering an unbiased perspective on the technology without promoting specific companies.
- Importance in Complex Cases: Emphasis will be placed on the significance of aligner material properties in complex cases, such as those involving extractions, with a focus on integrating these properties with staging and treatment design.
- Case Studies: The presentation will include examples of both successful and failed cases, providing insights on how to improve clinical outcomes in complicated orthodontic treatments.

Clear aligner therapy has revolutionized orthodontics, with recent advancements in 3D printing taking it even further. This presentation explores the remarkable biomechanical benefits of 3D printed shape memory aligners (SMAs).
The integration of 3D printing has transformed clear aligner therapy, enabling direct printing of SMAs using shape memory polymers. This not only streamlines production and enhances precision but also eliminates errors associated with traditional methods. Adjusting thickness and geometry reduces the need for attachments.
SMAs offer unique biomechanical advantages over thermoforming aligners, with their shape memory properties allowing for precise custom designs triggered by external factors like heat. This breakthrough in aligner geometry control marks a pivotal moment in clear aligner biomechanics.
The synergy of 3D printing and biomechanical innovations opens new possibilities in orthodontics, enabling precise tooth movements, even handling challenging rotations and translations for superior treatment outcomes.
This presentation emphasizes the extraordinary biomechanical benefits of 3D printed shape memory aligners, including precision, efficiency, patient comfort, and better results. The integration of technology and biomechanics has revolutionized treatment planning, offering discreet, comfortable, and sustainable alternatives to traditional aligners.
- Advancement in Clear Aligner Therapy: The integration of 3D printing with shape memory polymers has significantly enhanced clear aligner therapy, improved precision and reducing errors compared to traditional methods.
- Biomechanical Advantages of SMAs: 3D printed shape memory aligners (SMAs) offer unique biomechanical benefits, such as the ability to create precise custom designs that respond to external factors like heat, allowing for more controlled and effective tooth movements.
- Reduction of Attachments: The ability to adjust the thickness and geometry of SMAs through 3D printing reduces the need for additional attachments, simplifying treatment and improving patient comfort.
- Enhanced Treatment Outcomes: SMAs enable precise tooth movements, including challenging rotations and translations, leading to superior treatment outcomes compared to conventional thermoforming aligners.
- Revolution in Treatment Planning: The synergy of 3D printing and biomechanical innovations has revolutionized orthodontic treatment planning, offering more discreet, comfortable, and sustainable alternatives to traditional aligners.

- Treatment Limitations: While aligner therapy has advanced significantly with improvements in tray material and the use of attachments, certain aspects of tooth movement remain challenging compared to fixed appliances.
- Comparison with Fixed Appliances: The presentation will cover the pros and cons of aligner therapy relative to fixed appliances, particularly focusing on vertical control and biomechanical differences between the two methods.
- Mixed Dentition Cases: The use of aligners in mixed dentition cases will be discussed, highlighting specific considerations and challenges.
- Role of CBCT Data: The necessity of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) data in aligner therapy will be examined, emphasizing its importance for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Dental Monitoring: The presentation will address the benefits of dental monitoring in managing patients efficiently and effectively throughout aligner therapy.

- Advancements in AI: Next-generation artificial intelligence, especially deep learning, has made significant strides in medical image analysis, clinical diagnosis, and treatment decision-making.
- Limitations in Clear Aligner Technology: Clear aligner technology, though widely used in orthodontics, faces challenges due to the proprietary nature of appliance manufacturing. This results in closed processes for clinical data diagnosis, treatment planning, target position design, and aligner fabrication.
- Prof. Bai's Research Group: They are tackling these challenges by implementing a four-in-one open treatment process that utilizes deep learning technology to enhance every phase of clear aligner orthodontic treatment.
- Open Treatment Process: The approach allows orthodontists to independently select between hosted and chairside treatment processes, improving flexibility and control over the treatment.

The aim of this presentation is to describe the bone-anchored maxillary protraction (BAMP) and the derived new protocol mini-screw anchored maxillary protraction (MAMP) therapy. The dentoskeletal outcomes and the clinical indications of both MAMP will be discussed. Clinical trials have shown that MAMP therapy produced clinically relevant skeletal effects. MAMP might be an adequate treatment option for Class III growing patients in the early permanent dentition.
Take-home message
MAMP is preferably recommended for patients with mild to moderate maxillary deficiencies
- Bone-Anchored Maxillary Protraction (BAMP) Therapy: The presentation will discuss BAMP therapy, focusing on its approach and application in orthodontics.
- Mini-Screw Anchored Maxillary Protraction (MAMP) Therapy: Dr. Garib will present MAMP, a newer protocol derived from BAMP, using mini-screws for maxillary protraction.
- Dentoskeletal Outcomes: Short- and long-term outcomes of both MAMP and BAMP protocols will be demonstrated, highlighting their effectiveness and clinical results.
- Clinical Indications: The clinical indications for both therapies will be reviewed, with evidence showing that MAMP produces clinically relevant skeletal effects.
- Treatment Recommendation: MAMP is particularly recommended for patients with mild to moderate maxillary deficiencies, especially in the early permanent dentition.

- Feasibility of Immersive VR in Orthodontics: The work explored the feasibility of using 3D immersive virtual reality (VR) in orthodontics, a technology previously popularized by the gaming industry.
- Virtual Case Presentation Room: The initial application involved creating a virtual room for case presentations, enabling users to view and interact with case records in 3D, particularly useful during the pandemic when in-person meetings were not possible.
- Educational Tool: A second application was the development of a virtual room showcasing various types of malocclusions for predoctoral education, allowing dental students to compare this experience with traditional manual cast analysis.
- Patient and Student Preferences: Surveys revealed that both dental students and orthodontic patients preferred the immersive VR experience over traditional 2D screens and manual methods.
- Valid Applications: The studies confirmed that there are valuable applications for immersive VR technology in orthodontics, enhancing both educational and patient engagement experiences.

- Rising Demand for Aesthetic Orthodontics: There has been a significant global increase in the demand for aesthetic orthodontic treatments.
- Popularity of Lingual Orthodontics: While clear aligners are commonly used for adults in China, lingual orthodontics remains a reliable and popular option for treating a wide range of malocclusions, including cases requiring extraction, non-extraction, and orthognathic treatments.
- Focus of Presentation: The presentation will address clinical considerations specific to bimaxillary protrusion treated using the ribbon-wise lingual system.
- Key Considerations Discussed:
Biomechanical: Analysis of the mechanical aspects of treatment with the ribbon-wise lingual system.
Aesthetic: Considerations related to the aesthetic outcomes of using lingual braces.
Periodontal: Impact on periodontal health during and after treatment.
External Apical Root Resorption: Examination of root resorption issues associated with lingual orthodontic treatment.

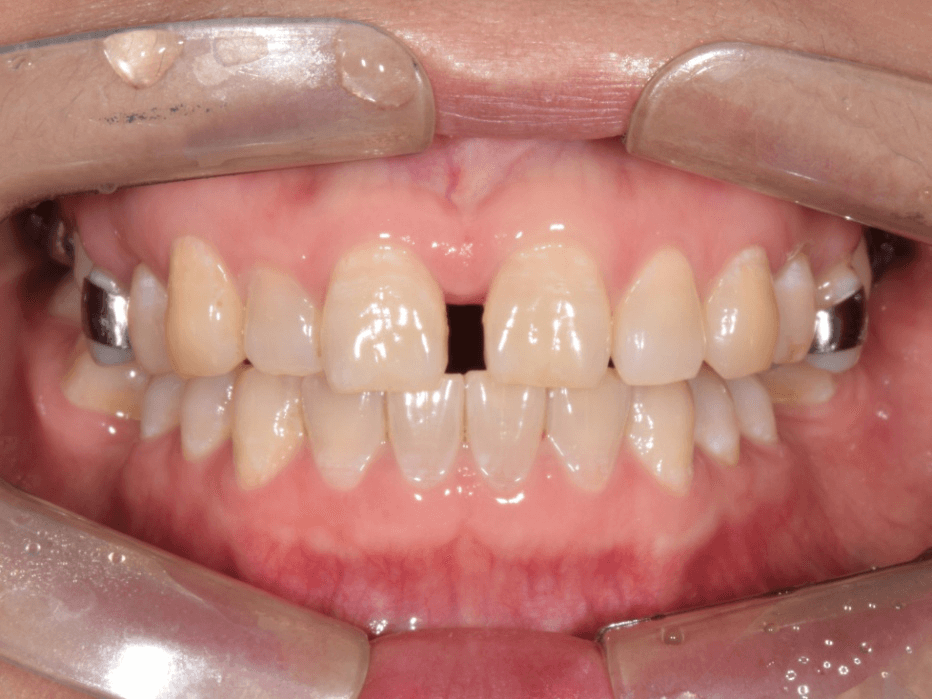
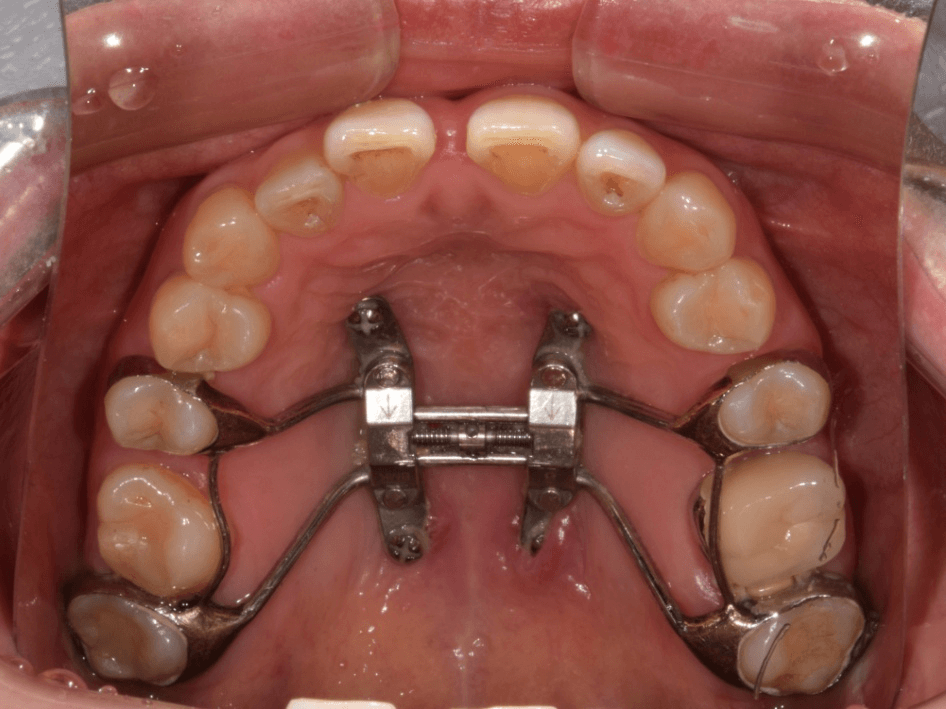
Transverse discrepancy is not easily recognized by the patient and the orthodontic envelope of discrepancy is reportedly narrow in the transverse direction, which is why surgically assisted palatal expansion is recommended for the correction of maxillary transverse deficiencies in grown-up patients. Miniscrew-assisted RPE (MARPE) has been suggested as an alternative to the surgical intervention. In the meantime, latest clinical reports revealed the gender- and age- dependent success rate of the MARPE in adults. Also limited amount of expansion and skeletal relapse have been claimed.
In this presentation, current status of the clinical outcome of the MARPE in postpubertal adults will be presented. Based on the suture biology, an expansion protocol to increase the success of the nonsurgical expansion will be demonstrated. Additionally, a gender- and age-specific treatment strategies will be proposed. Clinical cases indicating the use of MARPE for nonsurgical correction of Class III and asymmetry will be demonstrated. Troubleshooting in failure cases will also be explained. According to the theoretical background and clinical examples, nonsurgical approach for transverse correction can be justified under appropriate clinical manipulation to secure the quality and stability of occlusal outcomes.
- Recognition of Transverse Discrepancy: Transverse discrepancies are often not easily recognized by patients, and the orthodontic envelope of discrepancy is narrow in this direction.
- Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion: For correcting maxillary transverse deficiencies in adults, surgically assisted palatal expansion is commonly recommended due to its effectiveness.
- Miniscrew-Assisted RPE (MARPE) Alternative: MARPE has been proposed as a non-surgical alternative to surgical expansion. However, recent clinical reports have highlighted varying success rates depending on gender and age, as well as issues with limited expansion and skeletal relapse.
- Clinical Outcome of MARPE: The presentation will cover the current status of MARPE outcomes in postpubertal adults, including its effectiveness and limitations.
- Expansion Protocol: An expansion protocol based on suture biology will be demonstrated to enhance the success rate of nonsurgical expansion.
- Gender- and Age-Specific Strategies: The presentation will propose treatment strategies tailored to specific gender and age groups to improve MARPE outcomes.
- Clinical Cases and Troubleshooting: Clinical cases showcasing the use of MARPE for nonsurgical correction of Class III and asymmetry will be presented, along with strategies for troubleshooting failure cases.
- Justification for Nonsurgical Approach: The presentation will argue for the efficacy and stability of nonsurgical transverse correction approaches when appropriately managed, supported by theoretical and clinical evidence.

- Importance of Orthodontic Mini-Implants (OMIs): OMIs, also known as temporary anchorage devices, have become essential tools in orthodontic practice due to their ability to provide maximum or absolute anchorage, reduce patient compliance issues, and simplify treatment mechanics.
- Expanded Treatment Scope: OMIs enable orthodontists to work effectively in three-dimensional coordinates, expanding the range of orthodontic treatments.
- Factors Affecting Success Rates: While some factors influencing the success of OMIs are well-studied, others are often neglected. Understanding both well-researched and less-explored factors is crucial for optimal use.
- Biomechanical Understanding: Effective use of OMIs requires a solid biomechanical understanding to achieve efficient treatment results with minimal unwanted side effects.
- Presentation Objectives:
Current Use of OMIs: The presentation will showcase effective and efficient cases treated with OMIs.
Research Results: Findings from research on OMIs aimed at improving clinical outcomes will be discussed.
Future of OMIs: The presentation will explore potential future developments and innovations in the use of OMIs in orthodontics.

One of the frequent consequences of the severe periodontal destruction in patients with stage III and IV periodontitis is pathological tooth migration (PTM) with the subsequent functional and aesthetic consequences. The treatment of these patients must include periodontal therapy to arrest inflammation and attain periodontal health, but also the subsequent orthodontic and restorative treatments to restore the patient’s function and aesthetics.
In subjects with stage III–IV periodontitis, flaring of upper incisors, spacing / diastemas, and extrusion /overeruption due to missing teeth combined with occlusal trauma are common features of their secondary malocclusion. Therefore, a precise digital multidisciplinary treatment planning is crucial for the success restoration of these patients.
In this presentation it will be discussed the interdisciplinary digital diagnosis and treatment planning as well as the treatment sequence and follow-up of both periodontic, orthodontic, and restorative components. Evidence from clinical trials will be provided on how to stage periodontal and orthodontic therapies. Recommendations will be provided in regards the most appropriate orthodontic appliances, the type of biomechanics, the type of movements and the type of retention. Scientific evidence will be provided on the long-term prognosis of these patients and the specific influencing factors. Demonstrative cases will be presented.
- Pathological Tooth Migration (PTM): PTM is a common consequence of severe periodontal destruction in patients with stage III and IV periodontitis, leading to functional and aesthetic issues.
- Integrated Treatment Approach: Treatment must include:
Periodontal Therapy: To manage inflammation and achieve periodontal health.
Orthodontic and Restorative Treatments: To restore function and aesthetics after managing periodontal health.
- Common Features of Secondary Malocclusion: In patients with stage III–IV periodontitis, common features include:
Flaring of Upper Incisors
Spacing/Diastemas
Extrusion/Overeruption Due to Missing Teeth and Occlusal Trauma
- Digital Multidisciplinary Planning: Accurate digital diagnosis and treatment planning are essential for successful restoration. This involves coordinating periodontic, orthodontic, and restorative components.
- Treatment Sequence and Follow-Up: The presentation will cover:
Interdisciplinary Diagnosis and Planning
Treatment Sequence
Follow-Up Procedures
- Evidence from Clinical Trials: Data will be presented on how to stage periodontal and orthodontic therapies effectively.
- Recommendations: Guidance will be provided on:
Orthodontic Appliances
Biomechanics
oType of Movements
Retention Methods
- Long-Term Prognosis: Scientific evidence on the long-term prognosis of these patients and the specific influencing factors will be discussed.
- Demonstrative Cases: Clinical cases will be presented to illustrate the application of the discussed principles and treatments.

- Comprehensive Journey: The presentation outlines the process of developing orthodontic products from initial research and development to clinical implementation.
- Advanced Technologies: Focus on how contemporary technologies have transformed the orthodontic industry and improved the translation of innovations from the lab to clinical settings.
- Crucial Steps: Discussion of the essential steps involved in translating orthodontic technologies into practice, emphasizing the importance of each stage in the journey.
- Barriers to Transition: Exploration of the numerous obstacles that can impede the seamless integration of new orthodontic technologies into clinical use.
- Collaborative Efforts: Initiatives at the ADA Forsyth Institute to address these challenges through collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and industry stakeholders.
- Streamlining Innovation: The goal of fostering partnerships to streamline the path from technological innovation to practical clinical application.
- Advancing Orthodontic Care: Emphasis on how these efforts contribute to advancing orthodontic care and improving patient outcomes.

- Transformative Impact of AI: AI is set to significantly change healthcare practices and delivery methods.
- AI Applications Overview: The presentation will cover various AI-based applications within the healthcare sector.
- Challenges in Orthodontics: Specific issues related to the implementation of AI in orthodontics, both in research and clinical settings, will be addressed.
- Topics of Discussion:
Explainable vs. Interpretable AI: The distinction between AI systems that offer explanations for their decisions and those that provide interpretations.
Deep Learning Black Box Paradox: The difficulty in understanding how deep learning models arrive at their decisions.
Distribution Shift of Outcomes: Challenges arising from changes in data distribution that can affect AI predictions.
Predictive Analytics: The role of AI in predicting outcomes and trends in orthodontics.
Ethical Challenges: Ethical considerations and issues related to the use of AI in orthodontic practice.

Various methods for accelerating orthodontic tooth movement, both surgical and non-surgical, have been reported in the past 20 years. However, none of these methods have successfully provided a moderate level of evidence to support their efficacy. Studies demonstrating temporary positive outcomes during specific phases of orthodontic intervention have failed to establish their clinical relevance across the entire treatment period or to evaluate the potential complications and risks for relapse.
Is it scientifically justifiable to pursue accelerated tooth movement from a biological perspective? Does increased speed of tooth displacement necessarily lead to improved treatment outcomes? What ethical considerations come into play? Alternatively, shouldn’t we direct our efforts towards areas that can genuinely enhance patient well-being and elevate the standards of our profession?
In this lecture, I would like to delve into these considerations and discuss potential alternatives with you. I look forward to exchanging thoughts and gaining inspiration from our collective insights.
- Accelerated Tooth Movement Methods: Various methods for accelerating orthodontic tooth movement, both surgical and non-surgical, have been explored over the past 20 years.
- Lack of Robust Evidence: No method has provided moderate-level evidence supporting its overall efficacy. Temporary positive outcomes observed in specific phases have not consistently demonstrated clinical relevance or addressed potential complications and relapse risks.
- Biological Justifiability: The presentation will question whether pursuing accelerated tooth movement is scientifically justified from a biological perspective.
- Impact on Treatment Outcomes: Discussion on whether increasing the speed of tooth displacement necessarily leads to better treatment outcomes.
- Ethical Considerations: Exploration of the ethical implications of accelerating tooth movement and whether efforts might be better spent on areas that genuinely enhance patient well-being and elevate professional standards.
- Alternatives to Accelerated Movement: The lecture will propose potential alternatives and encourage a dialogue on how to improve orthodontic practices and patient care.

- The participant will have a better understanding of the four key trends driving this massive change impacting oral health care delivery
- The participant will learn how the patient and healthcare provider will transform drastically in the near future
- The participant will see visions of future technologies that will impact dental care delivery allowing more individuals to receive dental care and improving access to care

Organizers
Speakers
(Sorted alphabetically by name)

17th Floor Seminar Room
The ADA Forsyth Institute
245 First Street
(entrance to the building is at 1 Atheneum St)
Cambridge, MA 02142



40 Edwin Land Boulevard, Cambridge, MA 02142
The Royal Sonesta Boston is reserved exclusively for the 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth
International Orthodontic Symposium. You can directly arrange your
accommodation with the hotel using the link below to avail yourself of special rates.
ADA Forsyth Institute, 4.6 Miles

Sonesta Boston, 0.4 Miles

Boston is one of North America's most beautiful cities, offering visitors a unique blend of historical sites
and modern
attractions, beautiful waterfront views and lush parks, wonderful hotels and restaurants, and more exciting
events and
things to do and see than you can possibly fit into one visit.


Event: 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium
Date: Saturday, October 5th and Sunday, October 6th, 2024
USD $280 (Early-Bird Discount: Apr. 1 - Aug. 31)
USD $360 (Regular: From Sep. 1)
Payment Method: Paypal
Event: In-Person Registration - 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium
• A conference materials package
• 2 days of lunch and coffee/tea breaks
• 12 ADA CERP credit hours (Subject to the final program)
• IOF Membership: There is not cost to become an IOF member
• Cancellations:
Refund requests between Sep.1 and Sep.30 will incur a $50 cancellation fee.
Requests received after Sep. 30 will not be approved.
• Dress Code: Business Casual
• Food & Drink: Lunch and refreshments during the meeting will be provided for free.
• In consideration of being allowed to participate to the 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium, the IOF and their authorized agents are hereby released from any damages caused or incurred in connection with these activities. I agree to indemnify and hold the IOF and their authorized agents harmless against any liabilities, including reasonable attorney's fees, arising from, or in connection with, these activities.
• Program Changes: Events Organizers have the right to amend this program, as necessary. In the event of a cancellation, Events Organizers and their affiliates are not responsible for incidental costs incurred by registrants. We recommend purchasing refundable airline tickets.
In case of any question, please contact us at member@iofglobal.org
* I read and agree with IOF's Event Policies
* I read and agree with the Refund Policies
I need CE certification
I would like to be added to the ADA Forsyth Institute mailing list
Meet the Experts, Experience the Insights. Attend online for free, or join on-site to earn CE credits.
Don't miss out – register now and join me for this symposium!
https://www.iofglobal.org/ios2024

Payment Channel Closure Date: October 4th, 2024
Amount: USD $400 for 10 credits
Payment Method: PayPal
Before September 30th, 2024: Refund requests will incur a cancellation fee of USD 20.
Starting October 1st, 2024: Refund requests will not be approved.
Live Broadcast (October 5-6):
Accumulate 5 hours of online learning on each day (October 5 and October 6).
Complete and submit the survey questionnaire.
Replay Period (October 7-13):
Accumulate a total of 10 hours of online learning during the replay period.
Complete and submit the survey questionnaire.
All fees received by IOF will be fully paid to ADA Forsyth.
* I have read and agree to all the policies stated above.
Please add me to the IOF and ADA Forsyth Institute mailing list.

ADA Forsyth Institute designates this activity for 10 continuing education credits. Credits are awarded on actual attendance at individual sessions.
Concerns or complaints about a CE provider may be directed to the provider or to the Commission for Continuing Education Provider Recognition at ADA.org/CERP."
* Please add me to the IOF and ADA Forsyth Institute mailing list.
I am interested in becoming an IOF Member.

Register Information
With CE Credit
Legal Name:
Address:
Telephone Number:
Email:
Payment Results:

Register Information
Full Name:
Country/Region:
Degree:
Job Title:
Email:
Event: 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium
Date: Saturday, October 5th and Sunday, October 6th, 2024.
Additionally, this live streamed content will be available on-demand for 20 days after the Symposium for all registered virtual and in-person attendees.
We are looking forward to seeing you.




























